Nachrichtenartikel
Da der Handelskrieg im Westen entfacht, könnten aufstrebende Regionen Chancen für den globalen Handel bieten
Drei Monate im Jahr 2025 hat der globale Handel ein gewisses Maß an Widerstandsfähigkeit beibehalten, aber die Herausforderungen in der Lieferkette steigen, da die US-Handelspolitik schwerfällig und unberechenbar bleibt. Während die neue Welle von US-Zöllen im Vorschlaghammer-Stil, die Anfang April angekündigt wurden, die globalen Lieferketten in unbekannte Gewässer schickt, blickt QIMA’s vierteljährlicher Barometer auf die Lage der Beschaffungslandschaft im ersten Quartal eines weiteren beispiellosen Jahres zurück.
Handel Chinas mit aufstrebenden Regionen bleibt stark trotz Spannungen mit dem Westen
Chinas Wirtschaft bewies Widerstandskraft im ersten Quartal 2025, wobei sich Wachstumsprognosen Ende März optimistischer zeigten. Die eskalierenden Handelskonflikte mit den USA beeinträchtigen jedoch zunehmend die Beziehungen des „weltweiten Fabrik“ zu Käufern weltweit.
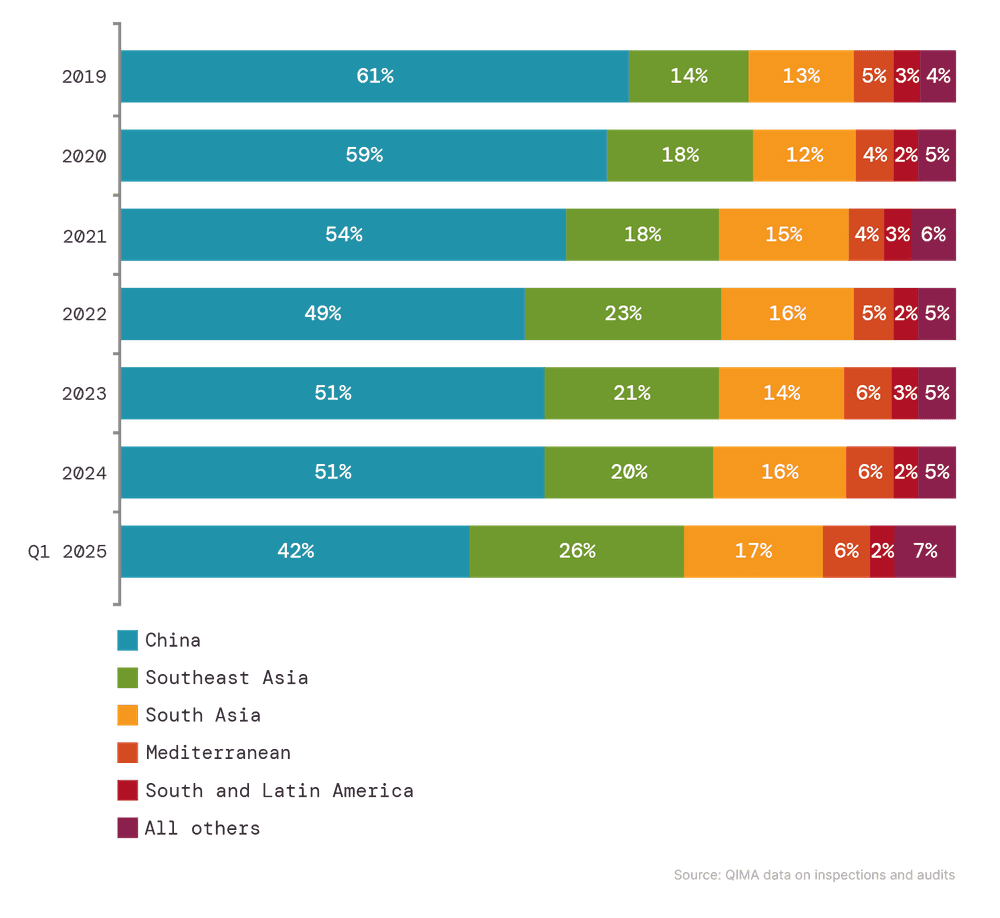
QIMAs Daten zum Inspektions- und Auditbedarf im ersten Quartal zeigen eine bemerkenswerte Verschiebung: Zum ersten Mal seit der Covid-Ära 2022 hat sich Chinas relativer Anteil in den Beschaffungsportfolios westlicher Käufer verringert. Dies deutet darauf hin, dass nordamerikanische und europäische Lieferketten ihre Anstrengungen intensivieren, um die Abhängigkeit von China zu reduzieren.
Gleichzeitig haben aufstrebende Volkswirtschaften eine starke Nachfrage nach Importen aus China aufrechterhalten. Unternehmen in Latein- und Südamerika treiben diese Nachfrage insbesondere an, die sowohl durch den lokalen Konsum als auch durch die auf US-Nearshoring ausgerichtete Produktion angeheizt wird.
US-Marken suchen neue agile Beschaffungspartnerschaften in ganz Asien
Trotz des Drucks durch Zölle haben US-Marken und Einzelhändler ihre Beschaffung aus China im ersten Quartal 2025 nicht signifikant reduziert (QIMA-Daten zu Inspektions- und Auditbedarf zeigen einen flachen Trend im Jahresvergleich). Sie lenken jedoch zunehmend zusätzliche Bestellmengen zu anderen Lieferanten-Hubs in Asien, als Teil der andauernden langfristigen Abkehr von China.
Bemerkenswerterweise haben traditionelle Alternativen zu China, wie Vietnam und Bangladesch, in diesem Quartal kein gestiegenes Interesse gesehen, wobei der Inspektions- und Auditbedarf in beiden Ländern im Jahresvergleich stagniert. In Vietnam könnte die Erwartung von Trumps gegenseitigen Zöllen zu dem verringerten Interesse beigetragen haben, während der Fokus von Bangladesch auf die Herstellung von Baumwolltextilien einige Optionen für Käufer einschränken könnte.
Statt dieser "üblichen Verdächtigen" erkunden US-Marken und Einzelhändler neue Beschaffungsmärkte in Südostasien: etwa Kambodscha (+36% YoY), die Philippinen (+62%) und insbesondere Indonesien, wo die Nachfrage nach Inspektionen und Audits von US-Unternehmen seit drei aufeinanderfolgenden Quartalen boomt und sich im ersten Quartal 2025 mehr als verdoppelt hat. Insgesamt hat die US-Nachfrage nach Inspektionen und Audits in Südostasien bisher 2025 um +55% zugenommen, wobei die Region für über ein Viertel aller US-Beschaffungen im ersten Quartal verantwortlich ist. Allerdings könnte die Auswirkung der jüngsten Zollerhebung—mit Vietnam und Kambodscha unter den am stärksten betroffenen—diesen Trend in den kommenden Monaten ändern.
Abb. 1. Relativer Anteil der Beschaffungsregionen in der Beschaffung für Käufer mit Sitz in den USA und der EU
Wachsende Konsumgütermärkte und Nearshoring-Projekte befeuern das Wachstum in Lateinamerika und Südamerika
Als eine der Regionen von Analysten hervorgehoben als wichtige Treiber des Handels im Jahr 2025, starteten Lateinamerika und Südamerika stark in das Jahr, sowohl als Import- als auch als Liefermarkt, was daran erinnert, dass der globale Handel nicht auf eine China-USA- oder China-EU-Route beschränkt ist.
QIMA-Daten zeigen, dass Unternehmen in Lateinamerika und Südamerika aktiv Quellen aus China im ersten Quartal 2025 erschlossen (Inspektions- und Prüfungsnachfrage um +21% Jahr für Jahr gestiegen), während sie auch andere Liefermärkte in Asien, wie Vietnam, Bangladesch und Indien, erkundeten. Auf der Angebotsseite erhielten die Hersteller der Region im ersten Quartal gesunde Auftragsvolumina, wobei Inspektions- und Prüfungsnachfrage um +15 % Jahr für Jahr zunahm, befeuert sowohl durch nordamerikanische Unternehmen als auch lokale Käufer
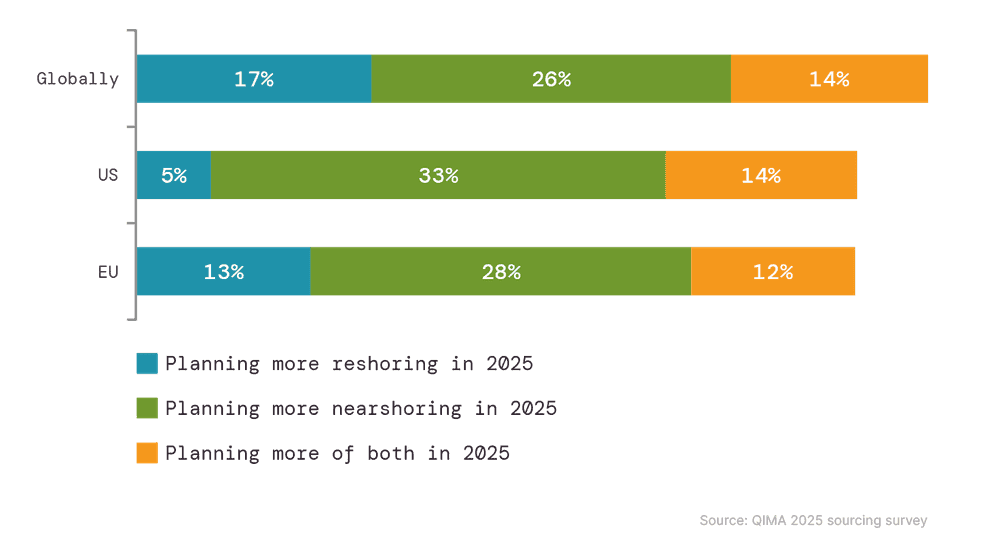
Mit nahezu 1 von 2 US-Unternehmen, die planen, in diesem Jahr das Nearshoring-Volumen zu erhöhen, könnten Importeure und Hersteller aus Lateinamerika und Südamerika in den kommenden Monaten weiterhin rege Aktivitäten sehen, insbesondere da der Druck durch Zölle auf die Region geringer ist als auf viele Übersee-Lieferantenzentren.
Abb. 2: Nearshoring- und Umschichtungspläne, die von den Befragten der QIMA 2025 Sourcing Survey gemeldet wurden
Angesichts von Unsicherheit und gemischter Verbraucherstimmung beziehen europäische Käufer weiterhin nahegelegene Märkte
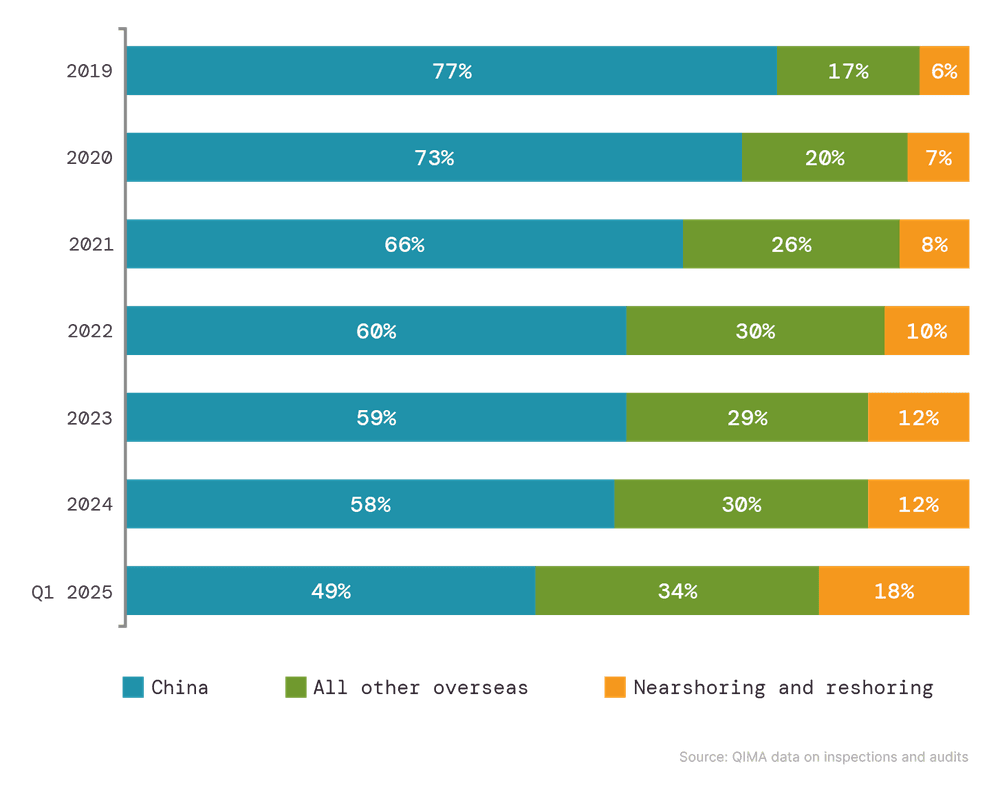
Die anhaltende Handelseskalation zwischen den USA und China beeinträchtigt auch die Beschaffungsstrategien globaler europäischer Marken mit Exposition gegenüber dem US-Markt, insbesondere im Modebereich. Dieser Welleneffekt hat, zusammen mit gemischtem Verbrauchervertrauen, dazu geführt, dass In der EU ansässige Unternehmen im ersten Quartal 2025 vorsichtig bei der Beschaffung in China sind. QIMA-Daten deuten darauf hin, dass diese Unternehmen auf bestehende Bestände zurückgreifen und in begrenztem Umfang hauptsächlich in der Nähe der Heimat nachbestellen.
Trotz des Rückgangs der Überseebeschaffung aufgrund der nachlassenden Nachfrage unterhielten europäische Marken und Einzelhändler ihre Beschaffungspartnerschaften innerhalb von Nahbeschaffung- und Heimregionen. Die Nachfrage nach Inspektionen und Audits stieg in den gut etablierten Lieferantenzentren der EU im Mittelmeerraum, einschließlich Marokko (+45% Jahr für Jahr), Tunesien (+32% Jahr für Jahr) und Ägypten (+66% Jahr für Jahr), und verdoppelte sich nahezu in Kontinentaleuropa. Diese Verschiebung erhöhte den relativen Anteil von Nahbeschaffung und Umschichtung in den europäischen Beschaffungsportfolios auf ein Allzeithoch im ersten Quartal 2025
Abb. 3: Relativer Anteil von Übersee- gegenüber Heimregionen in der EU-Beschaffung
Nicht-transparente Lieferketten beeinträchtigen die Fähigkeit der Käufer, sich in einem turbulenten Handelsumfeld zurechtzufinden
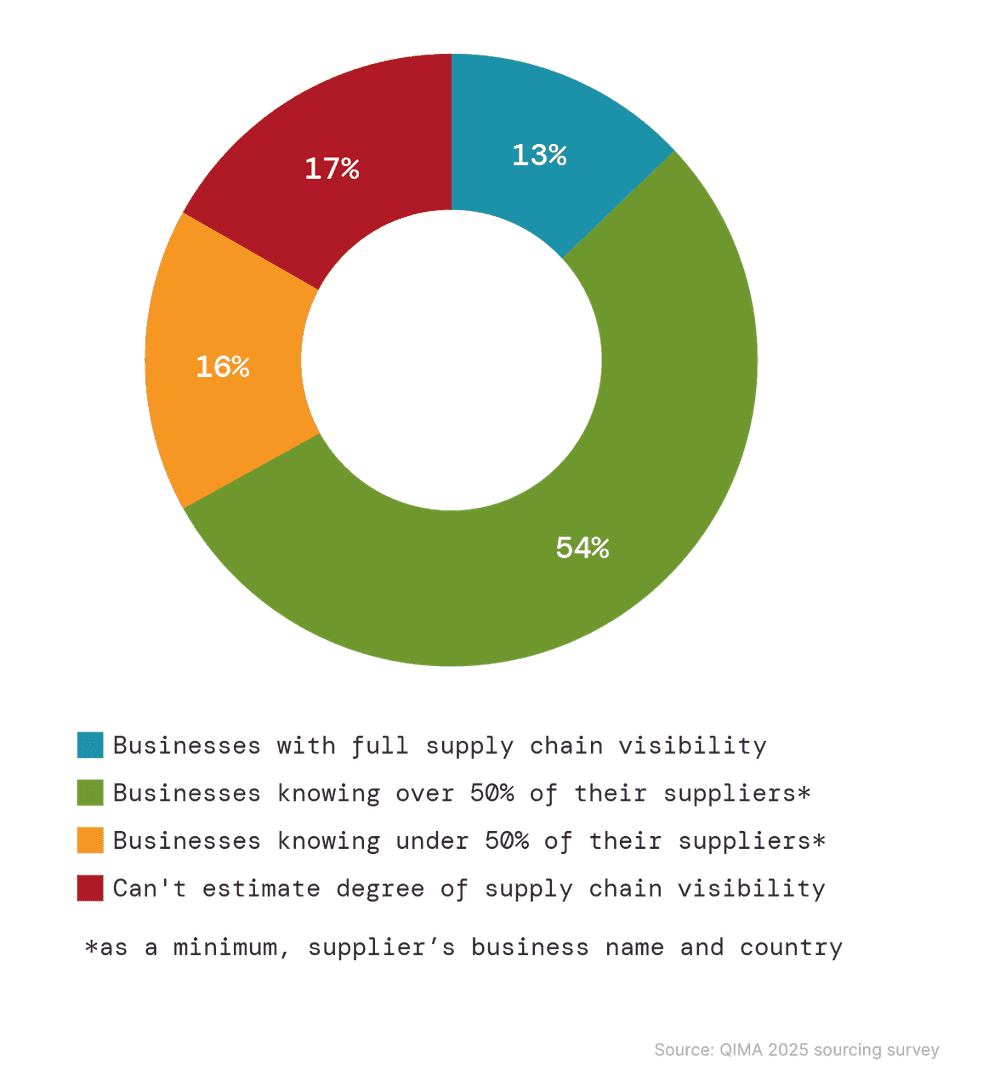
In der jüngsten QIMA-Umfrage von über 600 Unternehmen gaben nur 13% der weltweit Befragten an, volle Sichtbarkeit ihrer Beschaffungsnetzwerke zu haben, einschließlich Rohstofflieferanten. In bestimmten Industrien, wie der Elektronik, lag dieser Prozentsatz noch niedriger. Zusätzlich zu den erhöhten Risiken von Menschenrechtsverletzungen und Umweltproblemen führt dieser alarmierende Mangel an Transparenz in der Lieferkette dazu, dass es für Unternehmen schwieriger wird, rechtzeitige und informierte Beschaffungsentscheidungen zu treffen – eine zunehmend entscheidende Fähigkeit im volatilen Handelsumfeld von 2025.
Abb. 4: Selbsteingeschätzter Stand der Lieferkettensichtbarkeit, 2025